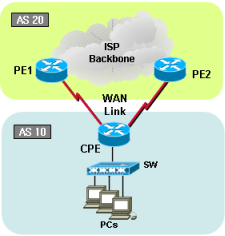
Cisco dual BGP with AS prepend (Load-Balancing)
|
|
[Traffic flow]
[CPE/Customer Cisco Router]
Current configuration:
!
version 12.x
!
hostname CPE
!
interface Ethernet0
description to Internal network
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0ip address 10.1.0.129 255.255.255.128 secondary
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mroute-cache
!
interface Serial0
description to ISP A – WAN 1
ip address 12.1.3.1 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mroute-cache
no fair-queue
!
interface Serial1
description to ISP A – WAN 2ip address 12.1.4.1 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mroute-cache
no fair-queue
!
router bgp 10
no auto-summarynetwork 10.1.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0network 10.1.0.128 mask 255.255.255.128neighbor 12.1.3.2 remote-as 20
neighbor 12.1.3.2 version 4neighbor 12.1.3.2 prefix-list 1 out
neighbor 12.1.4.2 remote-as 20
neighbor 12.1.4.2 version 4
neighbor 12.1.4.2 route-map second_link out!
ip classless
!ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial1!ip prefix-list 1 seq 5 permit 10.1.0.0/24
!
route-map second_link permit 10
set as-path prepend 10 10
!line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
[PE1 / ISP Cisco Router]
Current configuration:
!
version 12.x
!
hostname PE!
!
interface Serial0
description to WAN 1
ip address 12.1.3.2 255.255.255.252
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mroute-cache
no fair-queue
!router bgp 20
no auto-summary
neighbor 12.1.3.1 remote-as 10
neighbor 12.1.3.1 version 4
neighbor 12.1.3.1 distribute-list 2 out
!
ip classless
!access-list 2 deny any <– no route sent
!line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
!
version 12.x
!
hostname PE
!
interface Serial1
description to WAN 2
no ip mroute-cache
no ip directed-broadcast
no fair-queue
!
no auto-summary
neighbor 12.1.4.1 remote-as 10
neighbor 12.1.4.1 version 4
!
ip classless
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
[Verifing output]
CPE# show ip bgp neighbors 12.1.3.2 ad
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 iTotal number of prefixes 1
CPE#
CPE# show ip bgp neighbors 12.1.4.2 ad
BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.1.0.128/25 0.0.0.0 0 32768 iTotal number of prefixes 2
CPE#CPE# show ip bgp neighbors 12.1.3.2 ro
Total number of prefixes 0
CPE#CPE# show ip bgp neighbors 12.1.4.2 ro
Total number of prefixes 0
CPE#PE1#show ip bgp nei 12.1.3.1 ro
BGP table version is 64, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.0.0/24 12.1.3.1 0 0 10 iTotal number of prefixes 1
PE1#PE2#show ip bgp nei 12.1.4.1 ro
BGP table version is 104, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.0.0/24 12.1.4.1 0 0 10 10 10 i
*> 10.1.0.128/25 12.1.4.1 0 0 10 10 10 iTotal number of prefixes 2
PE2#Internet#traceroute 10.1.0.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.1.0.11 PE1 (20.3.5.1) 20 msec 24 msec 28 msec
2 CPE (12.1.3.1) 48 msec * 64 msec
Internet#traceroute 10.1.0.129
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.1.0.1291 PE2 (20.4.5.1) 20 msec 28 msec 32 msec
2 CPE (12.1.4.1) 40 msec * 52 msec
If you have any questions, feel free to send email us at [email protected]. If you are looking for professional grade service, you might want to try our "BGP experts service". What is "BGP Experts service"? Click "BGP Experts" from the top menu option. You will find out what the "BGP Experts" and what we are doing here for.

Recent Comments