Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is one of the major protocols to achieve WAN connection redundancy. When you connect your network to Internet, BGP will be the easiest choice. Especially with two different Internet service providers (ISPs), BGP would be the only protocol you can choose.
Simple Cisco BGP Configuration by topology
I believe that the below topologies would cover the most of BGP configurations in real life. However, If you need a configuration for more specific topology, please send email me at [email protected].
The information in this article is based on Cisco Routers and GNS3 simulation tool. And used Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.x(x) and above.
Also, the BGP sample configuration were created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
We strongly recommend you to create a lab before applying prospective BGP configuration to production network.
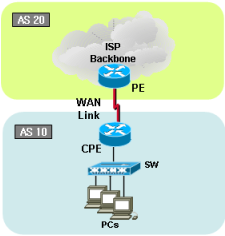
BGP topology 1 |
|
Sample configurations1-1-1. Cisco Single BGP with default route |
 |
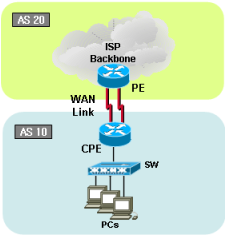
BGP topology 2 |
|
Sample configurations2-1-1. Cisco Single BGP with Multi-hop (load-balancing) |
 |
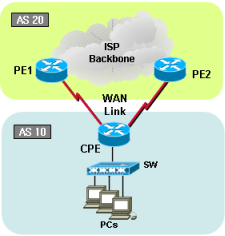
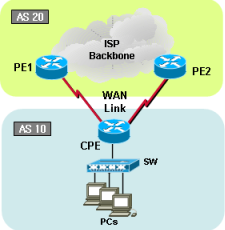
BGP topology 3 |
|
Sample configurations3-1-1. Cisco Dual BGP with Metric (Redundancy) |
 |
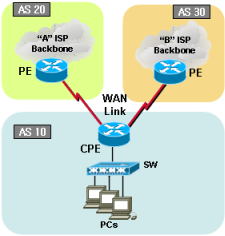
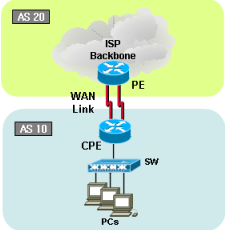
BGP topology 4 |
|
Sample configurations4-1-1. Cisco dual BGP with Metric (Redundancy) |
 |
BGP topology 5 |
|
Sample configurations5-1-1. Cisco dual BGP with AS prepend-HSRP (Load-sharing) |
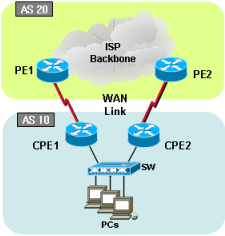 |
BGP topology 6 |
|
Sample configurations6-1-1. Cisco dual BGP with AS prepend-HSRP (Load-sharing) |
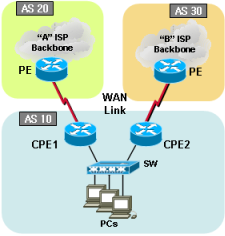 |
BGP topology 7 |
|
Sample configurations7-1-1. Cisco dual BGP with eBGP (Failover) |
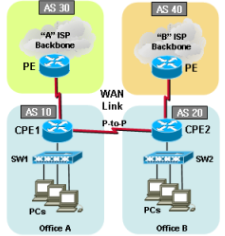 |
** Please Please link this article instead of copying or taking it without permission.
Thank you!

Recent Comments