Cisco dual BGP with AS prepend (Load-balancing)
|
|
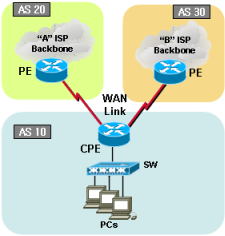
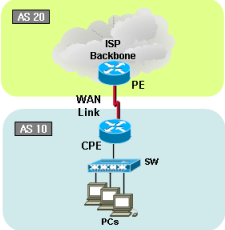
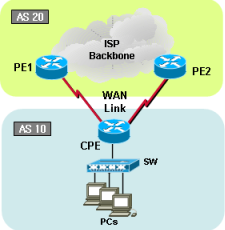
[Traffic flow]
In this sample, we are not receiving any BGP route table from ISP. We configured static routes are pointing to both serial links. Of cause it wouldn’t be 50/50, due to packets will be routed by destination based.
All traffic associated with 100.100.100.0/24 will be routed thru ISP_"A" and 200.200.200.0/24 will be routed thru ISP_"B". This configuration will cover failover situation as well. One of line failed, other link will take both traffic. See below example and testing output.
[CPE/Customer Cisco Router]
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname CPE
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
ip cef
no ip domain lookup
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial1/0
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address 10.20.1.1 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/2
ip address 10.30.1.1 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface FastEthernet2/0
ip address 200.200.200.1 255.255.255.0 secondary
ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
router bgp 10
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 100.100.100.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 200.200.200.0
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.20.1.2 remote-as 20 <—————— BGP neighbor to ISP_"A"
neighbor 10.20.1.2 prefix-list to-ISP out <——— Allow only IP block need to be advertised to ISP
neighbor 10.20.1.2 route-map traffic-1 out <—– Applied route-map on BGP session with ISP_"A"
neighbor 10.30.1.2 remote-as 30 <—————— BGP neighbor to ISP_"B"
neighbor 10.30.1.2 prefix-list to-ISP out <——— Allow only IP block need to be advertised to ISP
neighbor 10.30.1.2 route-map traffic-2 out <—– Applied route-map on BGP session with ISP_"B"
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip forward-protocol nd
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial1/1 <————- Load-sharing outbound traffic by destination
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial1/2 <————- Load-sharing outbound traffic by destination
!
ip prefix-list prefix-1 seq 5 permit 100.100.100.0/24
!
ip prefix-list prefix-2 seq 5 permit 200.200.200.0/24
!
ip prefix-list to-ISP seq 5 permit 100.100.100.0/24
ip prefix-list to-ISP seq 10 permit 200.200.200.0/24
!
route-map traffic-1 permit 10
match ip address prefix-list prefix-2
set as-path prepend 10 10 <——– Prepending ASN 10 two times to announcement(200.200.200.0/24)
!
route-map traffic-1 permit 20 <—— Necessary this statement in order to pass thru route(100.100.100.0/24)
!
route-map traffic-2 permit 10
match ip address prefix-list prefix-1
set as-path prepend 10 10 <——– Prepending ASN 10 two times to announcement(100.100.100.0/24)
!
route-map traffic-2 permit 20 <—— Necessary this statement in order to pass thru route(200.200.200.0/24)
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
[ISP_A PE/ISP Cisco Router]
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname ISP_A
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
ip cef
no ip domain lookup
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.20.1.2 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address 20.20.1.1 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/2
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
router bgp 20
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.20.1.1 remote-as 10 <—————— BGP neighbor to Customer
neighbor 10.20.1.1 route-map no-routes out <——- No BGP routes will be sent to Customer
neighbor 20.20.1.2 remote-as 20
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip forward-protocol nd
!
route-map no-routes deny 10 <——- No BGP routes will be sent to Customer
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
[ISP_B PE / ISP Cisco Router]
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname ISP_B
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
ip cef
no ip domain lookup
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 10.30.1.2 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/1
ip address 30.30.1.1 255.255.255.252
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/2
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial1/3
no ip address
shutdown
serial restart-delay 0
!
router bgp 30
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
redistribute connected
neighbor 10.30.1.1 remote-as 10 <—————— BGP neighbor to Customer
neighbor 10.30.1.1 route-map no-routes out <——- No BGP routes will be sent to Customer
neighbor 30.30.1.2 remote-as 30
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip forward-protocol nd
!
route-map no-routes deny 10 <——- No BGP routes will be sent to Customer
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
logging synchronous
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
end
[Verifing output]
CPE#sh ip bgp nei 10.30.1.2 ro
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 100.100.100.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 0.0.0.0 10.30.1.2 0 0 30 iTotal number of prefixes 1
CPE#sh ip bgp nei 10.20.1.2 ro
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 100.100.100.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 10.20.1.2 0 0 20 iTotal number of prefixes 1
CPE#sh ip bgp 200.200.200.0
BGP routing table entry for 200.200.200.0/24, version 6
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (100.100.100.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
CPE#sh ip bgp 100.100.100.0
BGP routing table entry for 100.100.100.0/24, version 5
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (100.100.100.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
CPE#
ISP_A#sh ip bgp neighbors 10.20.1.1 ro
BGP table version is 28, local router ID is 20.20.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.100.100.0/24 10.20.1.1 0 0 10 i
* 200.200.200.0 10.20.1.1 0 0 10 10 10 iTotal number of prefixes 2
ISP_B#sh ip bgp neighbors 10.30.1.1 ro
BGP table version is 32, local router ID is 30.30.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i – internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i – IGP, e – EGP, ? – incompleteNetwork Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 100.100.100.0/24 10.30.1.1 0 0 10 10 10 i
*> 200.200.200.0 10.30.1.1 0 0 10 iTotal number of prefixes 2
TR_A#sh ip bgp 100.100.100.0
BGP routing table entry for 100.100.100.0/24, version 22
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
10
10.20.1.1 from 20.20.1.1 (20.20.1.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
TR_A#sh ip bgp 200.200.200.0
BGP routing table entry for 200.200.200.0/24, version 23
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
50 30 10
20.50.1.2 from 20.50.1.2 (30.50.1.2)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external
30 10
20.30.1.2 from 20.30.1.2 (30.50.1.1)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external, best
TR_B#sh ip bgp 100.100.100.0
BGP routing table entry for 100.100.100.0/24, version 26
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
50 20 10
30.50.1.2 from 30.50.1.2 (30.50.1.2)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external
20 10
20.30.1.1 from 20.30.1.1 (20.50.1.1)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external, bestTR_B#sh ip bgp 200.200.200.0
BGP routing table entry for 200.200.200.0/24, version 24
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
2
10
10.30.1.1 from 30.30.1.1 (30.30.1.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
TR_B#
Internet#tr 100.100.100.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 100.100.100.21 20.50.1.1 68 msec 48 msec 32 msec
2 20.20.1.1 [AS 20] 20 msec 60 msec 32 msec
3 10.20.1.1 [AS 20] 16 msec 64 msec 72 msec
4 *
100.100.100.2 [AS 10] 60 msec 72 msec
Internet#tr 200.200.200.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 200.200.200.21 30.50.1.1 52 msec 36 msec 28 msec
2 30.30.1.1 [AS 30] 20 msec 64 msec 32 msec
3 10.30.1.1 [AS 30] 36 msec 40 msec 56 msec
4 *
200.200.200.2 [AS 10] 92 msec 100 msec
Internet#
[Dynamips testing]
Download and test it yourself with below Dynamips configuration files.
If you have any questions, feel free to send email us at [email protected]. If you are looking for professional grade service, you might want to try our "BGP experts service". What is "BGP Experts service"? Click "BGP Experts" from the top menu option. You will find out what the "BGP Experts" and what we are doing here for.


Recent Comments